In 2023, Jisc partnered with TeacherMatic to explore how AI-driven tools can enhance teaching productivity in higher education. Following a successful pilot in the Further Education (FE) sector, a new pilot was launched with seven Higher Education (HE) institutions to assess TeacherMatic’s ability to support teaching across different disciplines. This blog post provides an overview of the pilot, including its successes, challenges, and insights gained on the potential of generative AI tools in HE.
What is TeacherMatic?
TeacherMatic is an AI-powered platform that offers over 90 generators to assist educators in creating resources, including lesson plans, quizzes, rubrics, and more. The goal of the HE pilot was to assess the platform’s impact on reducing workload and enhancing teaching quality by leveraging generative AI in a wide range of subject areas.

Piloting TeacherMatic in HE
The pilot took place across seven HE institutions, including University College Birmingham, Stranmillis University College, University of Chester, University of East Anglia, University of Strathclyde, University of Sunderland, and the University of Westminster. Each institution received 50 licences, allowing participants to actively test the platform from January to July 2024. The pilot included two phases: phase one focused on training and an initial evaluation of the AI tool through focus groups, while phase two gathered feedback through questionnaires and pilot lead meetings.
Key Findings from Phase One
In focus groups at the end of phase one, we assessed TeacherMatic’s effectiveness in resource creation and teaching enhancement for HE. Participants delivering across various subjects and levels, from natural sciences to sports and technical disciplines, praised TeacherMatic for its time-saving capabilities, creativity support, and assistance with student feedback. Alongside the overall positive response, participants also noted areas for improvement, particularly the need for content generation at a higher level to better meet HE demands.
Key Positives:
- Time-saving tool: TeacherMatic significantly reduced the time spent on creating resources and generating ideas, such as lesson plans and presentation outlines.
- User-friendly: Most participants found it easy to use, especially for creating discussion topics and lesson plans.
- Enhanced teaching methods: TeacherMatic helped boost creativity and provided valuable starting points for teaching tasks.
- Remote teaching benefits: TeacherMatic was particularly useful for remote educators who couldn’t collaborate in person, helping to refine content and improve resource quality.
- Improved feedback: The feedback generator proved to be a time-saving feature, enhancing the quality of feedback provided to students.
Areas for Improvement:
- Complexity: Some users found TeacherMatic’s presentation content too basic for HE, with overly simple text and irrelevant images.
- Difficulty adjustment: The complexity slider didn’t always meet HE standards, often failing to generate sufficiently detailed content.
- Bloom’s Taxonomy: The tool’s use of Bloom’s Taxonomy lacked depth, especially when generating questions at higher cognitive levels like “analysis.”
Feedback from these focus groups has been shared with TeacherMatic, and the developers have responded positively, integrating it into their development roadmap.
Additional Insight:
Educators delivering online courses found TeacherMatic particularly useful for generating content and lesson planning, as they lacked the in-person collaboration opportunities available to onsite teachers.
Key Findings from Phase Two
In phase two of the TeacherMatic pilot, participants were surveyed to assess the tool’s suitability for HE.
Key insights from the Participant Questionnaire:
- Recommendation rate: 63% of participants would recommend TeacherMatic for HE use.
- Understanding AI: 86% of participants (43% strongly agreeing) felt the pilot enhanced their understanding of generative AI.
- Content quality: 51% rated the content produced by TeacherMatic as good.
- Learning enhancement: 69% reported that TeacherMatic improved learning experiences through feedback, assessments, and mentoring tools.
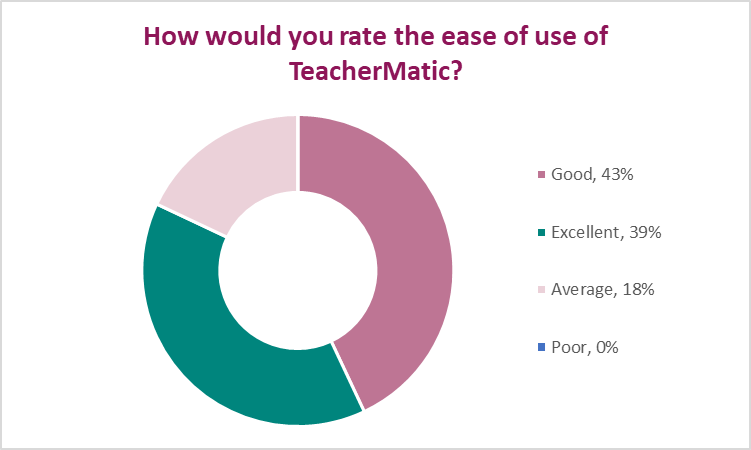
- Feedback on the ease of use for content generation with TeacherMatic revealed that 43% of participants rated it as good, 39% as excellent, 18% as average and 0% as poor.
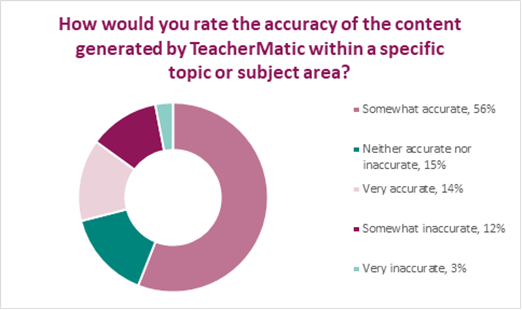
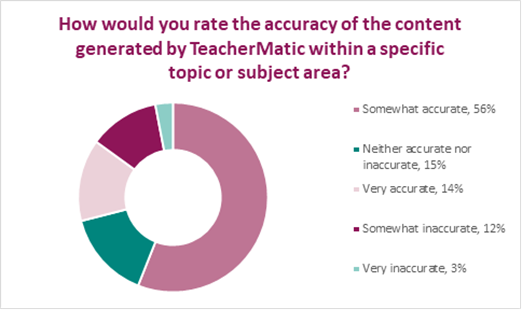
- When asked about the accuracy of content generated, 56% found it somewhat accurate, 15% found it neither accurate nor inaccurate, 14% very accurate, 12% somewhat inaccurate, while 3% found it very inaccurate.
- Complexity slider: Rated 3.7 out of 5 stars, with 52% giving it a 4-star rating.
- Learner Needs function: Rated 3.8 out of 5 stars for suitability in HE.
Engagement with TeacherMatic:
- Time-saving: 51% felt TeacherMatic saved them time in creating teaching resources, saving an average of 2 hours per week.
- Resource creation: Participants created an average of 18.1 resources using TeacherMatic, with popular tools including multiple-choice question generators and scheme of work creators.
- Some generators offer multiple input methods, and feedback collected showed the following usage patterns among participants: 55% used keywords, 37% used all three methods, 7% used the ‘upload a file’ function and 1% used the ‘URL’ function.
Pilot Lead Feedback:
- Workload reduction: TeacherMatic was effective in reducing workload for tasks like generating multiple-choice questions and summarising content, though the degree of impact varied.
- Content complexity: Some concerns were raised regarding the intellectual depth of content, particularly in specialised fields like law and advanced sciences.
- Collaboration and support: Regular training sessions and dedicated sharing platforms boosted the effectiveness of TeacherMatic.
- Broad use: Beyond teaching, TeacherMatic was used for drafting job adverts, policy statements, and mentoring students.
TeacherMatic’s Development Roadmap
The TeacherMatic team has responded positively to the feedback, and several improvements are already in progress:
- By October 2024, the complexity slider will be replaced with a more advanced system designed to produce outputs aligned with HE standards.
- In 2024, a new system is under development to replace the existing Bloom’s Taxonomy feature. This will include options to choose different pedagogical models, such as Rosenshine’s instructional principles and SOLO, as well as the ability to select sectors such as HE or FE, aimed at improving the specificity of outputs.
- Late 2024 will see an overhaul of the presentation generator, including better image integration and content depth. Users will soon have a more flexible tool that can generate comprehensive presentations tailored to different educational levels. Additionally, AI image generation will be integrated to supplement subjects not currently well-represented in the image library.
Summary
The TeacherMatic HE pilot demonstrated the platform’s potential to enhance productivity and creativity in HE. Despite the identified areas for development, the overall response was positive, with participants appreciating the platform’s capability to reduce workload and support teaching innovation. TeacherMatic’s commitment to ongoing improvement also highlights the potential for AI-driven tools to play an increasingly important role in HE.
As generative AI continues to evolve, platforms like TeacherMatic offer valuable insights into how technology can reshape the educational landscape.
Jisc’s Artificial Intelligence team recommendations
As the pilot showed, staff were able to save time compared to traditional methods. TeacherMatic is a well-suited product for HE and is supported by an experienced team within this sector. The pilot also showed that TeacherMatic is a suitable tool for building AI literacy among staff and exposing them to its capabilities in a controlled environment.
This report is also available as a pdf.
Find out more by visiting our Artificial Intelligence page to view publications and resources, join us for events and discover what AI has to offer through our range of interactive online demos.
For regular updates from the team sign up to our mailing list.
Get in touch with the team directly at AI@jisc.ac.uk
