AI Pilots at Jisc
A key area of the AI team’s work is running pilots of promising AI tools and products with Jisc members. These pilots provide our members with the opportunity to gain direct experience with AI-assisted tools, and the results provide valuable insights, which are shared with the sector.
Quicklinks
About the project
LearnWise
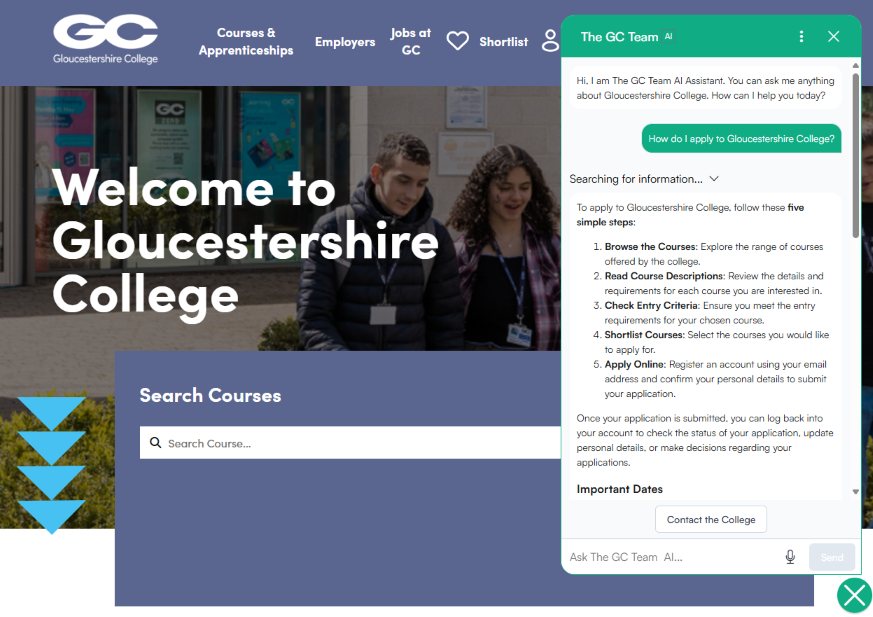
LearnWise is an AI-powered platform designed to streamline students’ access to support services. Each institution provides the knowledge base for their LearnWise assistant, allowing them to use their existing resources to finetune the chatbot to their context and set up the system to handle their specific use case.
LearnWise can be implemented across websites, ticketing systems, Virtual learning environments (VLEs), learning management systems (LMSs) and more. Their existing integration options are numerous and include popular platforms in education such as Sharepoint, Blackboard, Canvas, Moodle and many more. LearnWise can also host multiple implementations for one institution, meaning multiple AI assistants can be managed in one place.
These capabilities allow for a wide range of use cases from answering queries on how to submit assignments to offering guidance on course enrolment. Through the platform, more complex queries can also be escalated to the relevant staff teams, ensuring students receive efficient, personalised assistance.
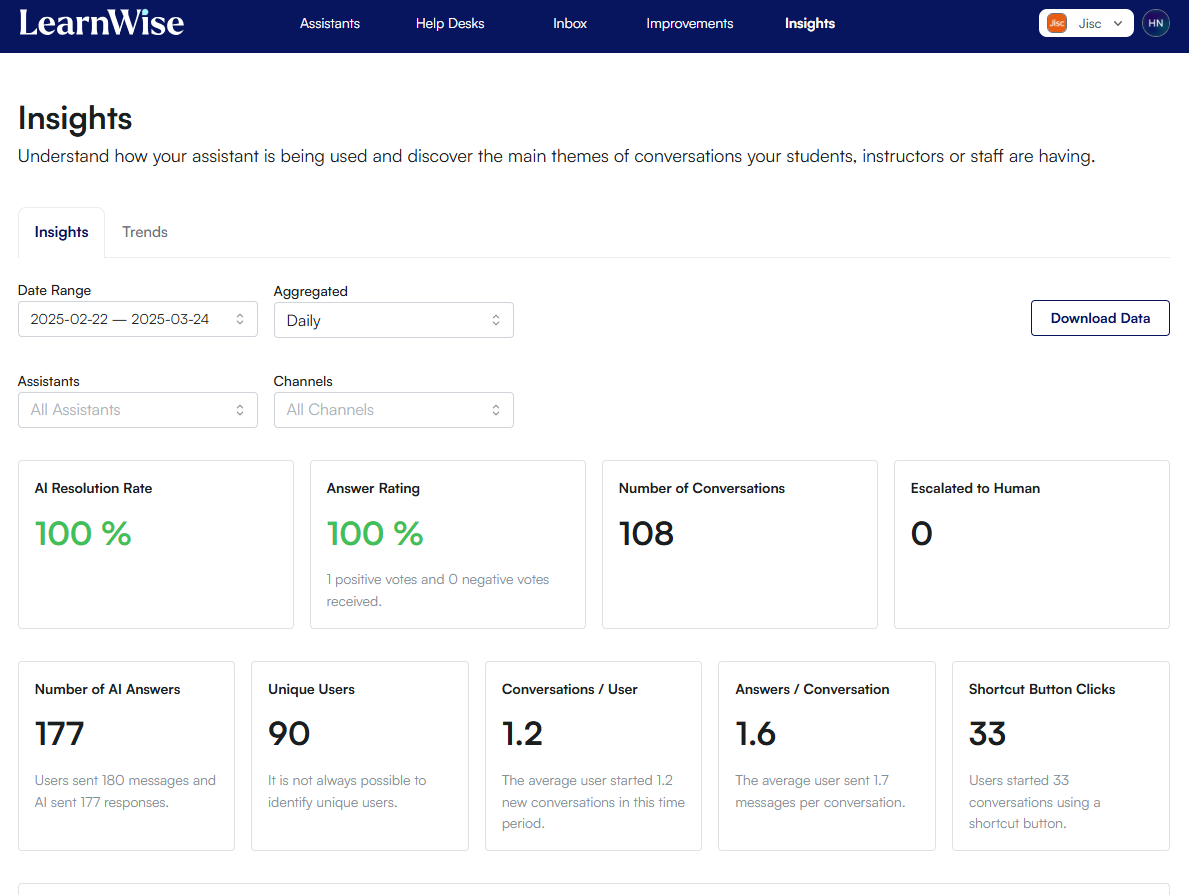
Behind the scenes an administrator portal provides a range of reporting features including access to the full chat logs of the AI assistant, data on the number of conversations and resolutions given by the AI or through escalation processes, and an improvements tool to support improvements to the knowledge bases used by the assistant.
LearnWise aims to make students’ lives easier whilst allowing institutions to gain deeper insights into what is driving user queries and where there are gaps in the support and content they have access to.
Participating institutions
Twelve institutions completed the project, piloting LearnWise between August and December 2024. These included eight further education colleges and four higher education institutions.
Thank you to our participants: Bath Spa University, Gloucestershire College, Kirklees College, Liverpool John Moores University, Neath College – NPTC Group of Colleges, Northern Regional College, Roehampton University, Shipley College, South Staffordshire College, The City of Liverpool College, University of Westminster, and Weston College.
How LearnWise was used
Pilot participants had full choice of where to implement their LearnWise AI assistant and many participants chose to add additional implementations during the pilot period, running multiple assistants at once. Though LearnWise is positioned primarily as a student support tool, several participants were interested in its capacity to support staff too and implemented assistants aimed at supporting staff CPD and more.
Due to the versatility of LearnWise the pilot was able to explore a range of use cases, these included:
- Supporting students’ pre-enrolment
- Supporting newly enrolled students with induction
- Student support queries
- Support students with course resources / course specific resources
- Enhancing staff support e.g., TEF framework, CPD
During the pilot, the AI assistant was situated on several different platforms, including:
- SharePoint
- Canvas
- Moodle
- Blackboard
- MyDay
Evaluation process
The evaluation sought to establish LearnWise’s effectiveness as a tool to improve support for students (and also staff where they were the end user). As well, it looked to evaluate whether use of LearnWise could increase the effectiveness and efficiency of relevant support services, including improving content management workflows at an institutional level.
All participants also took part in focus groups to gather staff feedback on the platform. Institution’s LearnWise usage statistics were also evaluated as a means of measuring engagement. A survey to collect further qualitative data was distributed where possible to end users of the AI assistant to gauge their experiences of the chatbots.
Insights from the evaluation
Objectives
The pilot institutions shared several common objectives, with many seeking to improve student support while reducing pressure on staff resources. One of the primary aims was to enhance access to information outside of office hours, providing students with immediate responses to common queries. Several colleges explicitly sought to test LearnWise as a tool for reducing administrative workloads, particularly in student services and welfare teams. Some were also interested in how their chatbot might help identify any changes needed in the resources it draws on, highlighting opportunities for improvements or expansion.
Another key objective was to assess institutional readiness for generative AI adoption. Several participants saw the pilot as an opportunity to gauge staff and student engagement with AI tools, with one institution aiming to excite the community about the possibilities of AI in a controlled, manageable way. Others positioned the pilot as an exploratory exercise, using it to determine whether chatbots could support broader digital transformation initiatives.
Concerns and Expectations
When asked about their concerns prior to implementing LearnWise, many institutions spoke of a general wariness around data protection and security, which applies to most technology projects. They were also keen to ensure that the chatbot could be easily integrated into existing platforms, without significant hassle.
Before the pilot, expectations regarding student engagement were mixed. While many believed students would find a chatbot intuitive and user-friendly, some institutions were sceptical based on past experiences with poorly performing chatbot solutions. Concerns were also raised about potential misuse, with one institution fearing that students might engage in frivolous or inappropriate interactions. Another significant challenge was managing expectations around AI capabilities, ensuring that staff and students understood the chatbot’s limitations while also recognising its potential.
A particularly noteworthy concern related to the chatbot’s ability to handle high-stakes queries, such as those involving mental health or safeguarding issues. One institution initially questioned whether the chatbot’s responses would be sufficiently sensitive and appropriate, but later reported that testing had alleviated these concerns, with responses proving to be well-calibrated and empathetic.
Questions were also raised about the impacts of implementing a digital assistant as part of the pilot, and then potentially taking the service away from users once the pilot had been concluded.
Strengths
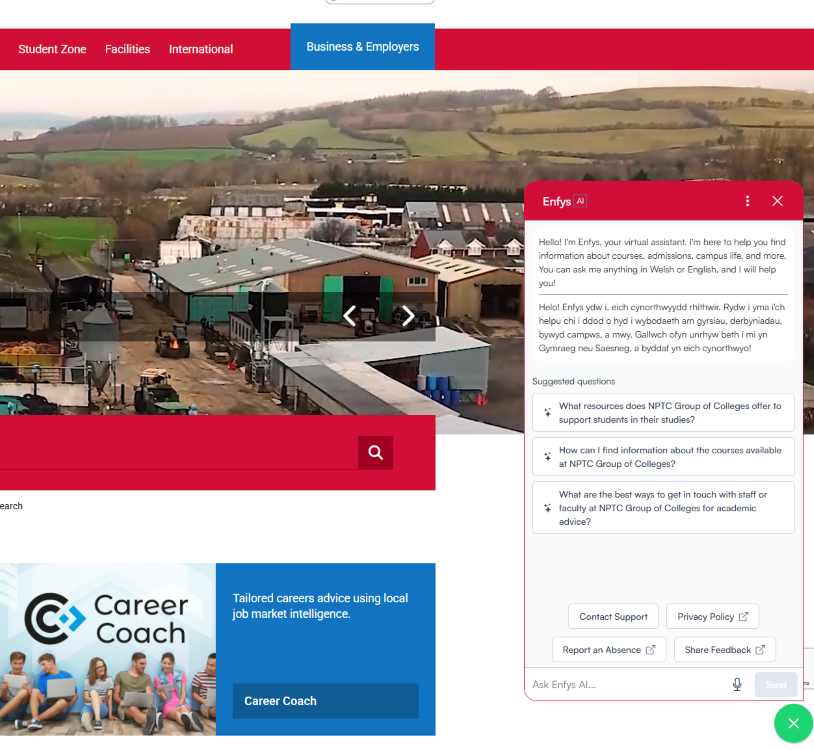
The majority of institutions found the technical setup process of their LearnWise chatbot to be straightforward and efficient, with several describing the integration as seamless. Participants appreciated the ability to customise their chatbots providing them with unique names, welcome messages and conversation shortcuts specifically written for their intended audiences. Institutions who implemented multiple chatbots appreciated the ability to manage them all from a single dashboard, ensuring a consistent user experience across different use cases.
Many also praised the LearnWise team for their responsiveness and support throughout the pilot, highlighting their willingness to address issues quickly and effectively. They felt that LearnWise were focused on the education sector and had a good understanding of sector needs, as well as being open to feedback and suggestions.
LearnWise was generally praised for its quick, clear answers and ability to pull relevant information from the sources it was given. Some institutions had previously encountered issues with chatbot “hallucinations” (incorrect or misleading responses), they reported that LearnWise performed reliably, with high levels of accuracy and professionalism and minimal hallucinations.
It was also noted that the chatbot’s escalation routes were well designed, enabling staff to set up referral information even for external services such as the Samaritans where necessary. This mitigated concerns from some participants around how suitable the chatbot would be at handling sensitive conversations.
A particular strength of the system was its ability to provide detailed performance analytics, allowing institutions to monitor chatbot interactions and refine responses accordingly. The improvements feature was found to be particularly useful, allowing adjustments needed to resources to be flagged and organised into a worklist. Some participants used insights from user interactions to widen the scope of resources provided to the chatbot too, for example adding mental health and wellbeing guidance to support vulnerable students.
Access to the conversations also provided some unexpected insights into users’ needs which could inform other support initiatives. For example, an institution who placed their LearnWise chatbot on their main website received queries from parents of prospective students which they did not anticipate. This provided insights into how the website itself was being used and what information visitors were looking for.
Student feedback revealed valuable insights about chatbot support benefits. One student particularly emphasised the importance of the chatbot’s non-judgmental nature compared to seeking human assistance. Additional feedback highlighted how the chatbot’s 24/7 availability and intuitive interface enhanced LearnWise’s accessibility for students. Overall, the chatbot’s ability to streamline student support was seen as a potential contributor to student retention, with some institutions identifying it as a long-term strategic benefit.
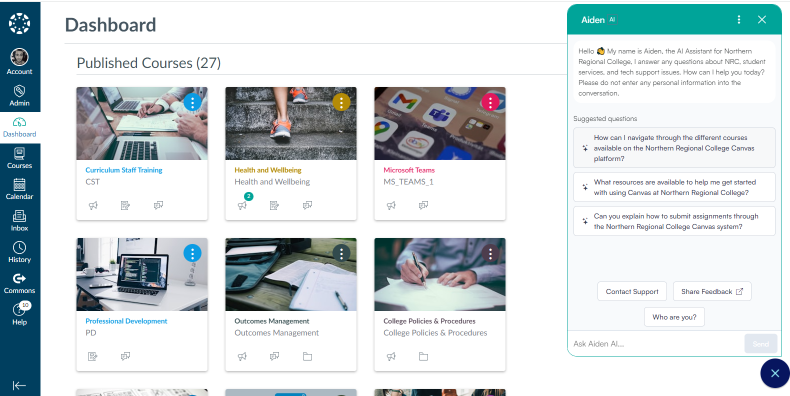
Staff use cases
Institutions who implemented staff use cases did note some additional challenges in preparing the resources to inform their chatbots with. Resources for students typically contained less sensitive information than those for staff and often might be stored in more ‘public facing’ areas which could be easily ‘scraped’ by LearnWise to inform the chatbot. Whereas staff facing resources were often stored in internal only systems, e.g., SharePoint which also contained sensitive data that could not be shared with the chatbot.
This meant more careful curation of resources to feed into the chatbot was required during the setup phase. In some cases, this limited the scope of queries the chatbot could handle as there was not capacity during the pilot to prepare the resources and this reduced its usefulness. This was reflected in some of the feedback from staff users. Overall, feedback indicated that LearnWise still had valuable impact on supporting staff with CPD and general professional practices in some instances by facilitating better navigation of professional development resources.
Suggested Improvements
A number of enhancements were proposed to increase engagement and refine the chatbot’s functionality.
Institutions recommended:
- Introducing role-based access controls within the admin portal
- Integrating the chatbot with MS Teams
- Mechanisms to encourage engagement, such as automated pop-ups after a short delay
- Expanding reporting capabilities to provide greater insight into usage trends
- Improving the handling of sensitive queries through more immediate flagging mechanisms
- Allowing greater flexibility in terms of the types of documents and files that could be inputted into the digital assistant’s knowledge base
- The ability to generate a wider range of outputs, such as podcasts, videos or presentations
How LearnWise is developing based on feedback
Introducing role-based access controls within the admin portal. At the time of writing LearnWise currently has this feature under development. Setting different permissions inside the LearnWise admin dashboard will ensure that various stakeholders can access only the information they require.
Integrating the chatbot with MS Teams. LearnWise has submitted their new MS Teams App to the Microsoft App Marketplace, this is currently being reviewed.
Mechanisms to encourage engagement, such as automated pop-ups after a short delay. LearnWise are in the design process for a proactive notification feature, which will allow admins to configure pop-ups to be issued from the chat assistant based on a variety of conditions (e.g., time on page, user role, and URL).
Expanding reporting capabilities. LearnWise has planned several improvements to the Insights feature, including data exports, a teacher-facing course-level dashboard, and filtered trend reports.
Improving the handling of sensitive queries through more immediate flagging mechanisms. This suggestion is being addressed by several different features. LearnWise has recently added a freeform search option to the Inbox in the admin panel, allowing admins to quickly identify and respond to sensitive conversations based on keywords. In addition, admins can define custom workflows that trigger escalation based on a set of conditions, for example if a student indicates they want to leave the institution they are prompted to speak to an academic counsellor.
Allowing more variety in the types of files added to the digital assistant’s knowledge base. Next to LearnWise’s growing library of integrations with external applications (e.g. Sharepoint, Kaltura, Panopto, Salesforce, ServiceNow, Topdesk, etc.), they are also planning to broaden file type support (various document types including audio and video).
The ability to generate a wider range of outputs, such as podcasts, videos or presentations. LearnWise plan to introduce the concept of widgets to the chat interface. These will be distinct UI components built to offer specific content types (e.g. videos) and interactions (e.g. multiple-choice quizzes).
LearnWise has a public roadmap available where you can check on the development of these updates and more.
Value for Money
A significant proportion of participants chose to continue using LearnWise after the pilot, which meant directly purchasing a subscription. This uptake is strong evidence that LearnWise represents good value for money – that said some institutions noted that the reason for purchasing subscriptions was to implement a wider rollout, which would allow for a more informed judgement on value for money in the long term, with many of the subscriptions being arranged for a limited amount of time.
For those who chose not to subscribe to LearnWise, reasons included the challenging financial circumstances, and uncertainty as to whether LearnWise’s benefits justified the cost.
Wider Views on AI
The pilot reinforced a broader interest in AI’s potential beyond chatbots, particularly in automating administrative tasks. However, there was also a recognition that AI tools must offer unique benefits that institutions cannot easily replicate themselves.
Concerns about data governance, ethical considerations including environmental impact, and the rapid pace of AI development led some institutions to hesitate before committing to long-term adoption. Several participants suggested that AI’s role in education would continue to evolve significantly in the coming years, making long-term investments in specific platforms more challenging.
Feedback on the Delivery of the Pilot
Feedback on Jisc’s role in the pilot was largely positive, with weekly meetups proving particularly valuable for many participants. A recommendation was made, however, to rebrand these sessions so that it was clear that they were for sharing best practices, rather than primarily troubleshooting.
Additionally, institutions requested clearer communication around offboarding at the end of the pilot, ensuring they were better prepared for the chatbot’s removal.
The short-term nature of the pilot also had some implications for user engagement. While some institutions acknowledged that adoption takes time, others expressed disappointment that interaction levels remained limited during the pilot, with the pilot’s short duration being seen as a key factor. This feedback will inform our future pilot projects.
Summary of feedback
Overall, feedback on LearnWise (both the platform and the organisation) was highly positive. Setup and implementation were relatively easy, and end users benefited from accurate and informative responses from their AI assistants. The team at LearnWise, meanwhile, reinforced the merits of their product with strong customer service. Attesting to participants’ satisfaction with LearnWise, eight out of twelve institutions have since committed to or are exploring extending their use of LearnWise beyond the pilot via paid subscriptions.
Considering the broader context of the sector’s journey in AI adoption, a key insight from the pilot was that advances in AI (in this case the development of large language models) are improving colleagues’ perceptions of AI’s efficacy. While many institutions highlighted initial concerns that the AI assistants may be incapable of responding to student queries with relevant, accurate and informative answers – these misgivings quickly dissipated as participants observed the quality of LearnWise’s interactions with learners.
Next steps
Following this pilot Jisc and LearnWise are pleased to advise the launch of a Learnwise AI Chest Agreement. Chest agreements provide preferential licensing agreements for software and online resources to the UK academic sector.
For institutions looking more broadly for advice on chatbots/digital assistants, Jisc will be publishing a series of guidance documents on implementing chatbots.
If you would like to find out more about LearnWise and insights from the pilot, please contact ai@jisc.ac.uk
Jisc’s AI team is continuing to run pilot projects of promising AI tools, access all of our completed pilot reports here. New pilot opportunities will be communicated through the AI in Education Jiscmail list and will be open to Jisc member institutions, sign up here to join the list.
Find out more by visiting our Artificial Intelligence page to view publications and resources, join us for events and discover what AI has to offer through our range of interactive online demos.
For regular updates from the team sign up to our mailing list.
Get in touch with the team directly at AI@jisc.ac.uk

