Following our pilot of TeacherMatic with eight Further Education (FE) colleges, we decided to explore its potential within the Higher Education (HE) sector. In early 2024, we launched a new pilot with seven universities: University College Birmingham, Stranmillis University College, University of Chester, University of East Anglia, University of Strathclyde, University of Sunderland and University of Westminster. The primary goal of this pilot is to assess how TeacherMatic’s generative AI capabilities can be leveraged to create innovative teaching and learning content while simultaneously reducing the workload for educators.
What is TeacherMatic?
TeacherMatic is an AI-driven platform engineered to leverage generative AI technologies to support educational staff by automating content creation. The platform aims to reduce workloads and time by generating various educational resources, including assessment rubrics, discussion prompts, and ideas for laboratory activities. Since its initial introduction, TeacherMatic has expanded its capabilities significantly, incorporating numerous new generators and features like Microsoft Single Sign-On functionality.
About the pilot
The HE pilot is structured similarly to our FE pilot, consisting of two phases. Phase one began in January which included comprehensive training for all participants, and concluded in March. This initial phase was intended to provide participants with their first experience using TeacherMatic, allowing them to assess and review the generated content. The second phase is scheduled to run from April to the summer of 2024. During this time, participants will have the opportunity to further engage with the AI tool and continuously evaluate its effectiveness and capabilities.
Where are we now?
At the end of phase one, we met with each participating university and held focus groups with five – ten users from each. The discussions centred on key questions designed to assess whether TeacherMatic saves time, how easy it is to use, and the quality of the content it creates. These sessions aimed to determine if the generated content is appropriate and useful for Higher Education settings.
Feedback from focus groups:
Usability
Feedback from the focus groups indicates that TeacherMatic is straightforward and user-friendly. Additional support is readily accessible through small blue icons that offer example prompts for using the generators.
However, some participants said they had some challenges navigating due to the number of generators available, which can make it hard to find what they are looking for. Others shared they found it easier to use the search function at the top and filters on the left.
Feedback around the usability and learning many said TeacherMatic has made the experience of using generative AI more approachable, as it allows them to generate content and learn about its limitations firsthand without needing to learn how to prompt well.
Level of content
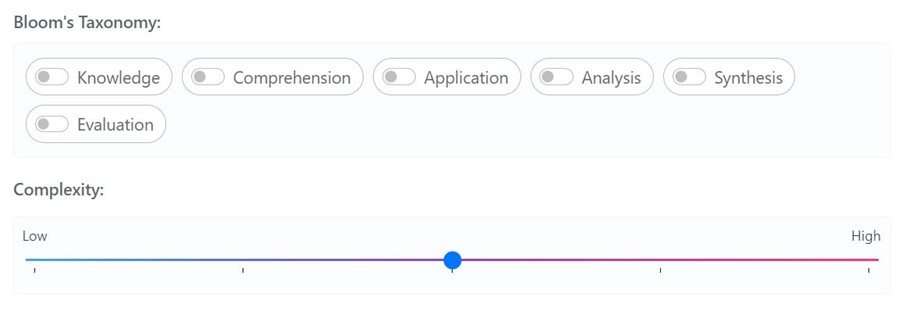
One of the pilot aims was to find out whether TeacherMatic can generate content appropriate for HE and how well the complexity slide works. The feedback on this has been mixed. For general, non-specific topics like project management, marketing, and general debate topics, the AI tool has been able to produce content that is mostly relevant and often at a sufficiently high level. However, participants felt that for specific topics the AI tool does not generate suitable content for HE level when using the complexity slider. The example subjects provided were UK Law and Mechanical Engineering. I think it is important to highlight the capabilities AI tools use large language models which are trained on vast amounts of training data and if the training data has not been included about a particular topic, then the results will be mixed.
Interestingly though, several participants said that they could generate content at a higher level by using the “Chat with TeacherMatic AI” generator by having a conversation and providing a more detailed prompt. Some participants also felt that they were able to generate content at a more suitable level by utilising other chatbots, however, they acknowledged that users would require proficient AI literacy and prompting skills to do this.
Quality of generated content
Aside from the level, the feedback on the quality of the generated content was generally positive. Participants appreciated the variety of downloadable file formats and the abundance of ideas generated around topics. Many shared that the content provided a solid foundation for creating teaching and learning resources suitable for HE. Discussions also highlighted how the diversity of generators is beneficial in sparking ideas, particularly when considering how to offer differentiation teaching and learning.
The use of the rubric generator received positive feedback, many use it as a reviewing tool and said it has helped them to improve the clarity of their assessment for learners. Feedback regarding the PowerPoint generator was less positive. For example, users noted that it often generates blocks of text that are not at a suitable academic level for higher education. Additionally, there were concerns about irrelevant images being included in the generated content.
Potential to save time
Feedback about the potential to save time was mixed. Many participants felt that TeacherMatic can indeed save time when planning resources and content, particularly in developing multiple-choice questions, summaries, glossaries, and debates. However, they also pointed out that while TeacherMatic helps in generating initial content quickly, this content often serves as a starting point. The generated material, although helpful, typically requires further adjustments and adaptations to ensure it meets the needs of HE.
Participants said the availability of functions is excellent. For example, being able to create multiple-choice questions from a YouTube URL was highlighted as particularly useful. One participant explained that they upload the lecture presentation each week using the Classroom Questions generator create a series of questions and use these as a seminar starter.
Several participants mentioned that the email generator had saved them time. The most common comment was that TeacherMatic helps the initial stages of topic exploration and planning. Overall, TeacherMatic is seen as a useful assistant that has enabled some participants to utilise generative AI.
Summary
Over the next few months, participants will continue to use TeacherMatic and will provide more detailed feedback at the beginning of summer. The insights from phase one have been interesting, particularly to see how TeacherMatic is being used in the HE space compare to FE. We’ve seen more participants utilising the “Chat with TeacherMatic” than in FE, as participants said that this generator with more prompting could generate content at a suitable level for HE. On the other hand the number of generators and features TeacherMatic offers help to add variety even to those who initially felt overwhelmed by the technology. This first phase has revealed that while the complexity slider may struggle to generate appropriately advanced content for more specific topics, it excels with general topics.
Find out more by visiting our Artificial Intelligence page to view publications and resources, join us for events and discover what AI has to offer through our range of interactive online demos.
For regular updates from the team sign up to our mailing list.
Get in touch with the team directly at AI@jisc.ac.uk